In the quest for sustainable agriculture, harnessing the incredible potential of microbes has emerged as a game-changer. Microbes, such as bacteria and fungi, play a pivotal role in the health of both soil and plants. This blog post explores the fascinating world of microbes and their ability to unlock a world of success for farmers. Join us as we delve into the science, benefits, and challenges of using microbes in agriculture.
The Microbial Marvels
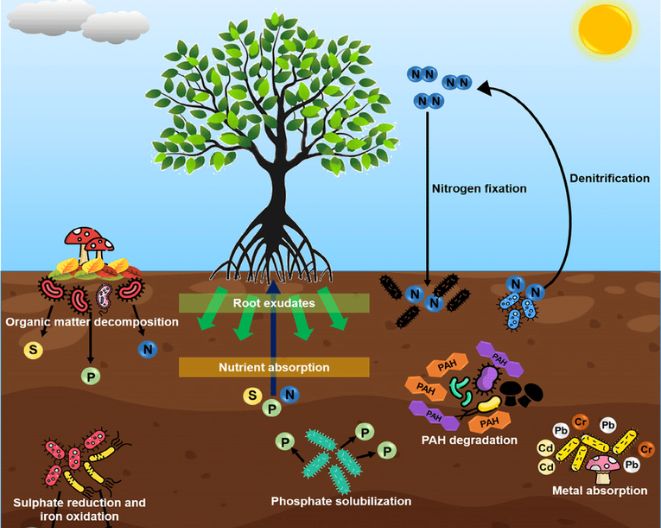
1. Microbes 101: Who Are They?
To appreciate the impact of microbes, it’s essential to understand who they are. Microbes, short for microorganisms, are tiny living entities invisible to the naked eye. They include bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms that form the foundation of life on Earth.
2. The Soil Microbiome
Soil is a bustling ecosystem teeming with microbes. The soil microbiome comprises a diverse community of microorganisms that interact with each other and the environment. They perform essential functions like nutrient cycling, disease suppression, and maintaining soil structure.
The Microbial Magic: Benefits for Crops
1. Nutrient Cycling
Microbes are the unsung heroes of nutrient cycling. They break down organic matter, releasing vital nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, making them available to plants. This natural recycling process reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers.
2. Disease Suppression
Certain beneficial microbes act as a natural defense mechanism for plants. They out-compete harmful pathogens, protecting crops from diseases without the need for chemical interventions.
3. Enhanced Nutrient Uptake
Microbes can form symbiotic relationships with plant roots, creating mycorrhizal networks that improve the plant’s ability to absorb water and essential nutrients. This leads to healthier, more robust crops.
4. Soil Structure Improvement
Microbial secretions help bind soil particles together, enhancing soil structure. Well-structured soil allows for better water infiltration and root growth, ensuring healthier and more productive plants.
Challenges in Harnessing Microbes
1. Lack of Awareness
One major challenge is the limited awareness and understanding of the role of microbes in agriculture. Many farmers are unaware of the benefits of microbial applications.
2. Quality Control
Ensuring the quality and viability of microbial products can be challenging. Maintaining the viability of live microbes during production, packaging, and application is crucial for success.
3. Compatibility with Conventional Practices
Integrating microbial solutions into existing farming practices can be tricky. Farmers often need to adapt their routines and approaches to fully leverage the benefits of microbes.
4. Research and Education
More research and educational efforts are needed to support the practical application of microbial solutions in diverse agricultural settings. This includes identifying which microbes work best for different crops and soils.
Success Stories: Real-World Applications
1. Biofertilizers
Biofertilizers containing nitrogen-fixing bacteria have shown tremendous promise. They convert atmospheric nitrogen into a plant-available form, reducing the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers.
2. Mycorrhizal Inoculants
Mycorrhizal fungi inoculants are increasingly used to enhance plant nutrient uptake. These beneficial fungi form a symbiotic relationship with plants, improving their resilience and growth.
3. Microbial Pesticides
Biological pesticides made from beneficial microbes are becoming a popular choice for pest and disease management. They are eco-friendly and don’t harm beneficial insects.
Case Studies: Microbes in Action
1. Reviving Degraded Soil
A farmer in California used mycorrhizal fungi to restore soil health in a previously degraded vineyard. The improved soil structure and nutrient cycling resulted in healthier grapevines and increased yields.
2. Sustainable Rice Farming
In India, farmers are adopting biofertilizers with nitrogen-fixing bacteria for rice cultivation. This sustainable approach has reduced the need for synthetic fertilizers, benefiting both the environment and their budgets.
3. Disease Control in Organic Farming
Organic strawberry growers in Oregon successfully manage fungal diseases by applying microbial biopesticides. This has allowed them to maintain organic certification while protecting their crops.
Making Microbes Work for You
1. Soil Testing
Start with a comprehensive soil test to determine the microbial activity in your soil. This will guide your microbial application strategy.
2. Microbial Product Selection
Consult with experts or agronomists to choose the right microbial products for your specific crops and soil conditions.
3. Application Techniques
Follow recommended application guidelines for the chosen microbial products. Proper application is critical for success.
4. Monitor and Adapt
Regularly monitor the progress of your crops and soil. Be prepared to adapt your microbial application strategy based on the results and changing conditions.
Conclusion
Microbes are a key to unlocking success in agriculture. Their ability to improve soil health, enhance nutrient cycling, and protect crops from diseases is a testament to their potential. While challenges exist, with the right knowledge and approach, farmers can harness the power of microbes to cultivate bountiful crops and foster thriving soil, ushering in a more sustainable and productive future in agriculture.